CDNs, or Content Delivery Networks, have transformed how websites handle performance and user experience. But while they can turbocharge loading speed and user satisfaction, their effect on search engines isn’t always straightforward. This article breaks down the real advantages and disadvantages of CDN in acceleration and search engines to help developers, marketers, and businesses make informed decisions.
How CDNs Accelerate Website Performance
How CDNs Work to Reduce Latency and Boost Speed
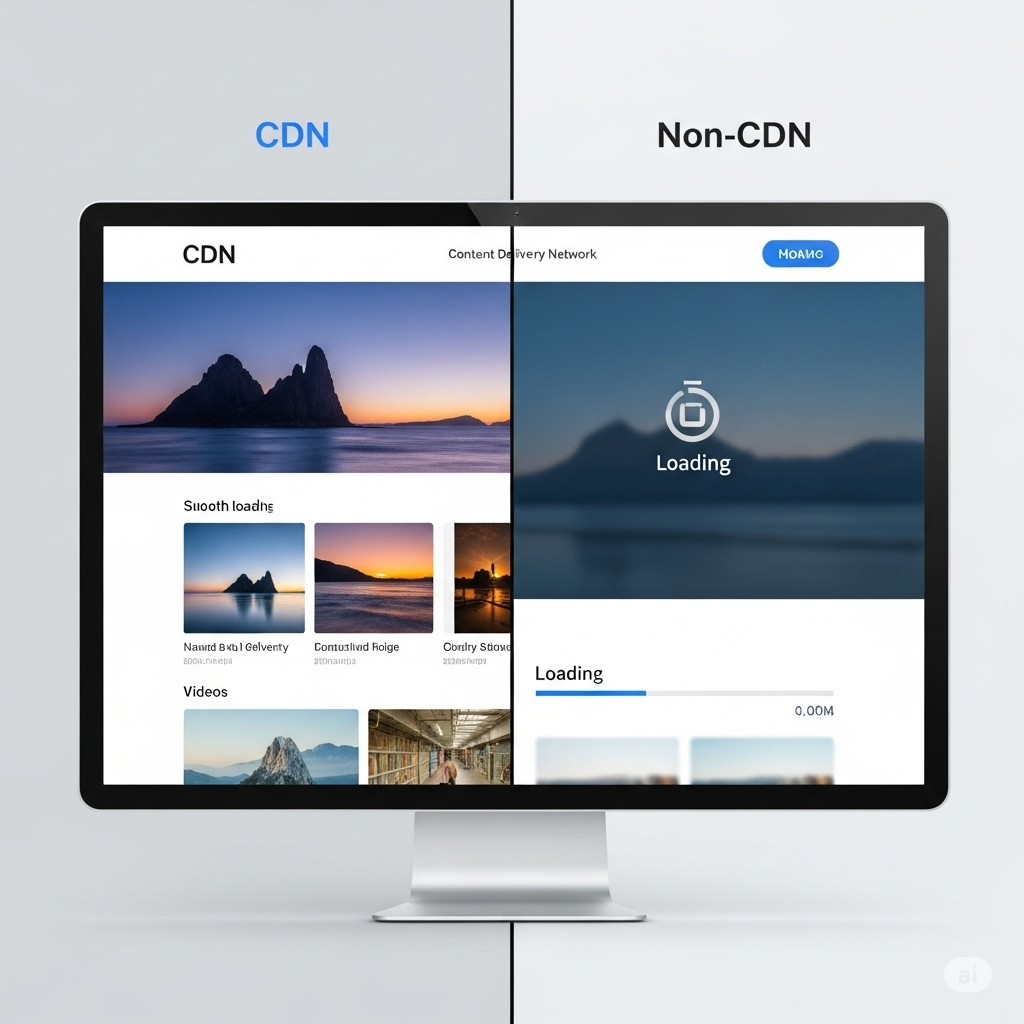
A CDN works by distributing your website’s static content across multiple servers located worldwide. When a user accesses your site, the CDN serves content from the nearest server, minimizing the distance data travels and thereby reducing latency. This decentralized model is especially effective for websites with a global audience.
Geographic Distribution for Faster Content Delivery
By caching images, stylesheets, scripts, and even entire pages at edge locations, CDNs eliminate bottlenecks caused by centralized hosting. Users in Europe no longer have to wait for content from a server in North America, which significantly improves load times and responsiveness.
Advantages and Disadvantages of CDN in Acceleration and Search Engines
Primary Benefits of CDN for Acceleration and SEO
The key advantage of using a CDN lies in site speed. Faster sites mean lower bounce rates and longer session durations, both of which positively impact search engine rankings. Google’s algorithm considers page speed as a ranking factor, so the indirect SEO benefit of acceleration is substantial.
Potential SEO Pitfalls from Improper CDN Configuration
While CDNs offer speed, misconfigured implementations can harm SEO. Duplicate content, incorrect canonical headers, or problems with crawl accessibility may confuse search engines. If bots crawl the CDN version instead of the canonical site, it can cause indexing issues.
Impact of CDN on Core Web Vitals
How CDN Usage Affects LCP, FID, and CLS
CDNs significantly improve Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) by reducing load times for significant assets, such as images or videos. First Input Delay (FID) and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) also benefit, particularly when the CDN supports optimized JavaScript delivery and layout stability.
Meeting Google’s Page Experience Standards with a CDN
Google’s Core Web Vitals are essential metrics for ranking. A well-implemented CDN helps meet these goals by optimizing the time to first byte (TTFB), compressing files, and utilizing HTTP/2 or HTTP/3. Without these, even high-quality content may struggle in rankings.
CDN and Its Influence on SEO Crawling Efficiency
How CDNs Can Help or Hinder Search Engine Bots
A properly configured CDN enhances crawl efficiency by improving server response times and reducing timeout errors. However, CDNs that block bots or throttle traffic during high load can prevent search engines from indexing content effectively.
Managing Robots.txt and Crawl Directives with CDNs
To avoid SEO setbacks, it’s crucial to sync robots.txt files and meta directives across both your origin server and the CDN. Discrepancies may lead to unintended indexing of test environments or blocked resources that are essential for rendering pages correctly.
Advantages and Disadvantages of CDN in Acceleration and Search Engines for Global Sites
Speed Gains for International Audiences
Global businesses benefit the most from the deployment of a CDN. Load balancing and regional replication minimize international latency, which is crucial for e-commerce and service-based platforms serving multiple countries.
SEO Localization Challenges
However, international CDNs can interfere with geo-targeting if IP-based detection redirects users incorrectly or if hreflang tags are not correctly handled. Search engines may serve the wrong regional version to users, resulting in both UX and SEO issues.
CDN’s Role in Reducing Server Load and Downtime
Protecting the Origin Server During Traffic Spikes
A CDN absorbs much of the traffic, preventing your central server from becoming overwhelmed during flash sales or viral campaigns. This reliability ensures consistent uptime and better search engine rankings, as search engines prioritize site stability.
Downtime Risks When CDN Services Fail
The downside is CDN dependency. If the CDN provider experiences an outage or misconfiguration, your site might become unreachable globally. Redundancy and fallback plans are crucial for avoiding catastrophic SEO consequences.
The Effect of CDN on Security and HTTPS SEO Signals
Improved HTTPS Handling and Security Protocols
CDNs often include SSL termination, making it easier for websites to implement HTTPS. Since HTTPS is a known ranking factor, CDNs contribute positively by ensuring secure content delivery with minimal configuration from the site owner.
Risks of SSL Misconfiguration on CDNs
However, if SSL is not correctly configured or if the CDN uses shared certificates, browsers may show security warnings. This undermines user trust and SEO performance due to increased bounce rates.
CDN Caching Strategies and SEO-Friendly Delivery
Optimizing Cache-Control Headers for Search Engines
Caching static content improves speed, but it’s essential to manage cache-control headers so that search engines always retrieve the latest version of your content. Stale content might mislead both users and crawlers.
Avoiding Duplicate Content Through Proper Caching Rules
To prevent SEO penalties, ensure the CDN doesn’t cache duplicate versions of the same content with different URLs or parameters. Canonical tags, consistent URLs, and smart caching rules can avoid this issue entirely.
Analytics and CDN: A Complicated Relationship
How CDNs May Distort Analytics Data
Because CDNs serve cached pages, traditional analytics tools might record fewer hits or misattribute traffic sources. This affects your ability to accurately measure actual performance and the success of your SEO campaigns.
Solutions for Tracking Real User Behavior Behind a CDN
To maintain accurate analytics, integrate client-side tracking and make sure your analytics scripts aren’t cached or blocked. Using tools that support CDN environments helps preserve the integrity of your data.
Choosing the Right CDN for Your SEO Goals
Matching CDN Features to SEO Requirements
Look for a CDN that supports edge SEO features, such as header rewriting, gzip compression, mobile content optimization, and full HTTPS support. Additionally, verify that it integrates seamlessly with your CMS and supports SEO-friendly configurations.
Avoiding Vendor Lock-In and Platform Limitations
Avoid CDNs that limit custom configuration or lack transparency in URL rewrites and header management. A flexible CDN ensures your SEO strategy remains in your control rather than being dictated by platform constraints.
Conclusion: Should You Use a CDN for Speed and SEO?
The advantages and disadvantages of CDN in acceleration and search engines must be weighed carefully. CDNs undeniably boost speed and performance, directly impacting the user experience and indirectly enhancing SEO. However, without correct implementation and ongoing monitoring, they can cause indexation issues, duplicate content problems, or even site outages.
If you’re running a global website, a CDN is almost a non-negotiable requirement. For local or niche sites, the decision should consider technical capabilities, traffic patterns, and SEO priorities. CDNs are powerful—but they require proper configuration and vigilance to fully realize their benefits without risking your search visibility.