Website hijacking is no longer a distant cyber threat—it’s happening now, targeting businesses of all sizes. Understanding how to prevent website hijacking is critical for protecting your brand, customers, and revenue streams. This guide outlines essential strategies to secure your website infrastructure against modern hijacking methods in 2025 and beyond.
Understanding Website Hijacking
What Is Website Hijacking and How It Works
Website hijacking refers to the unauthorized control or manipulation of a website, typically used to steal data, redirect traffic, or distribute malware. Attackers can hijack domains, sessions, browser behavior, or entire hosting accounts. The goal is to compromise either user trust or system integrity for profit or sabotage.
Common Types of Website Hijacking
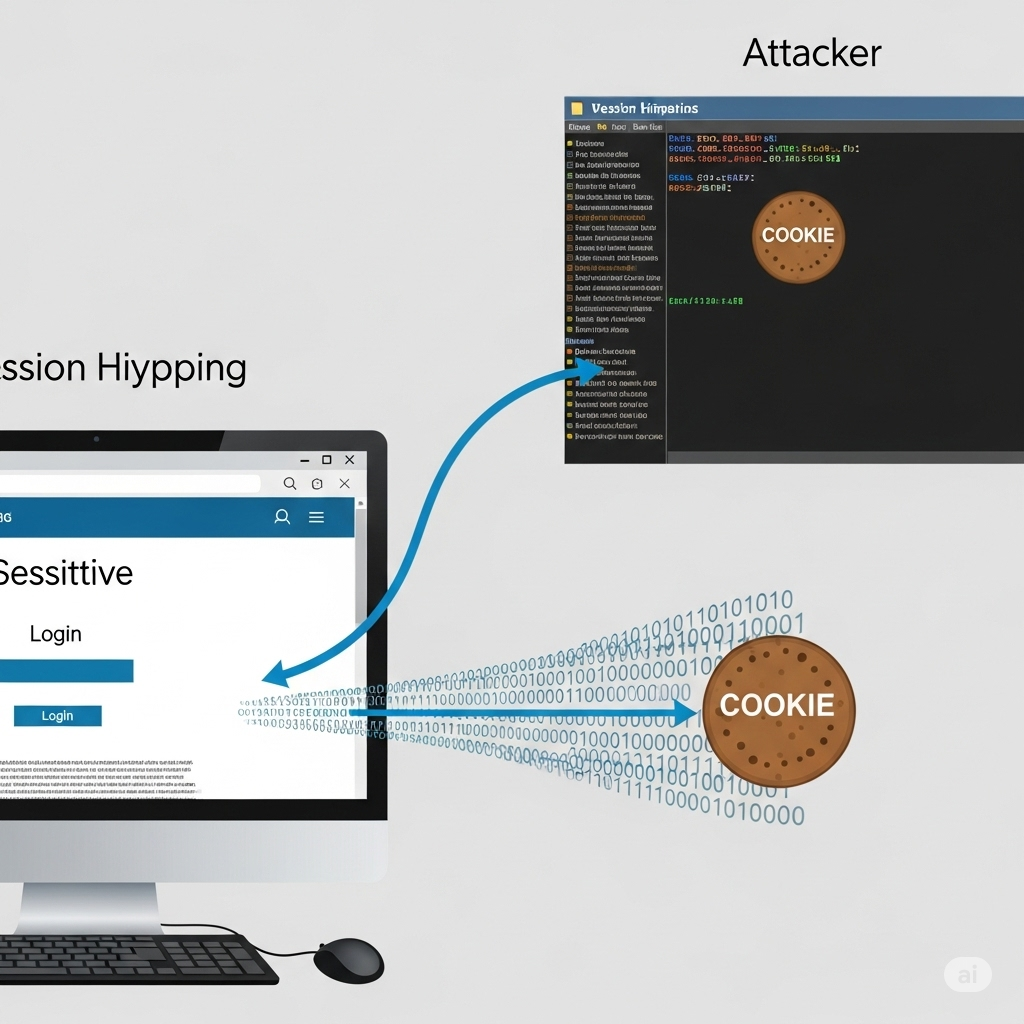
Session hijacking involves stealing session cookies to impersonate users. Domain hijacking occurs when attackers gain access to domain registrar accounts. DNS hijacking redirects users to malicious IPs. CMS hijacking targets vulnerabilities in platforms like WordPress. Each type requires unique mitigation tactics.
How to Prevent Website Hijacking by Securing DNS Infrastructure
Why DNS Configuration Is a Prime Target
DNS is the backbone of web traffic routing. If hijacked, all incoming traffic can be silently redirected. This makes DNS one of the most exploited attack vectors.
Best Practices to Secure DNS
Use registrar-level locking to prevent unauthorized changes to your domain. Enable DNSSEC to add cryptographic authentication. Restrict DNS record editing rights within your organization to prevent unauthorized changes to DNS records. Regularly audit all DNS records for unauthorized changes.

How to Prevent Website Hijacking with Strong Authentication Controls
Implementing Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Adding 2FA to all admin panels, hosting platforms, and domain registrars ensures that even if passwords are compromised, unauthorized access is blocked. Use TOTP apps or hardware keys rather than SMS for maximum protection.
Role-Based Access Control
Restrict website admin features based on user roles. Not every team member needs full backend access. Define least-privilege policies and review permissions quarterly to limit attack surfaces.
Monitoring and Detecting Suspicious Activities in Real-Time
Importance of Continuous Monitoring
Hijacking can happen within minutes. Real-time monitoring allows quick responses before attackers can cause lasting damage. Failure to detect breaches promptly can result in damage to SEO, blocklisting, or brand loss.
Tools and Tactics for Monitoring
Deploy intrusion detection systems (IDS) on hosting environments. Use website integrity monitoring tools that alert you to unauthorized file changes. Monitor server logs for unusual traffic patterns or geolocation access.
Website Hardening Tactics to Prevent Code Injection Attacks
Blocking Common Web Exploits
Websites are vulnerable to XSS, SQL injection, and remote file inclusion (RFI). To prevent hijacking through these vectors, use a Web Application Firewall (WAF), sanitize all input fields, and disable unnecessary PHP functions.
Security Headers and Content Policies
Implement HTTP security headers such as Content-Security-Policy (CSP), X-Frame-Options, and Referrer-Policy. These limit the browser’s ability to execute malicious code or embed your site in phishing pages.
SSL Certificates: A Double-Edged Sword
SSL Hijacking and Mitigation
Even with HTTPS, if a user’s session is intercepted (via rogue Wi-Fi or outdated browsers), SSL hijacking can occur. Use HSTS (HTTP Strict Transport Security) to force secure connections. Enable OCSP stapling to ensure real-time certificate integrity.
Choosing the Right Certificate Authority
Always choose a reputable Certificate Authority (CA). Use Extended Validation (EV) or Organization Validation (OV) certificates to add an additional layer of trust and prevent impersonation by attackers issuing fraudulent certificates.
How to Prevent Website Hijacking via Third-Party Integrations
Risks of External Scripts and Plugins
Third-party scripts, plugins, and analytics platforms can become hijack vectors if compromised. Many attackers inject malicious JavaScript through outdated integrations or dependencies.
Managing Third-Party Risks
Regularly audit all external scripts and dependencies. Self-host critical libraries when possible. Use Subresource Integrity (SRI) to ensure scripts haven’t been tampered with. Set up alerts for plugin updates and patch them immediately.
Session Management Strategies to Prevent Hijacking
Securing User Sessions
Session hijacking occurs when attackers steal session tokens. Implement secure cookie flags (HttpOnly, Secure, and SameSite). Ensure sessions expire after inactivity and are tied to IP or device fingerprints.
Token Rotation and Session Validation
Use rotating tokens and short session lifetimes. Validate user actions by comparing session timestamps or device metadata to ensure accuracy and reliability. Log out users after a specific inactivity period or on unusual device behavior.
How to Prevent Website Hijacking by Conducting Regular Penetration Testing
The Role of Ethical Hacking
Penetration testing simulates real-world attacks to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in a system. This proactive approach helps identify misconfigurations and outdated software before attackers do.
What to Test During Penetration Audits
Focus on authentication systems, DNS setup, CMS core and plugins, third-party scripts, and hosting permissions. Also, test for known CVEs (Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures) relevant to your tech stack.
Human Factors and Training to Prevent Hijacking Attacks
Employee Mistakes Are Common Gateways
Phishing remains a top hijacking method. One careless click can result in complete control of the website being lost. Human error accounts for a large percentage of successful hijacks.
Building a Security-First Culture
Train employees to identify phishing emails, fake login prompts, and social engineering attempts. Run simulated attacks to test responses. Make security awareness part of onboarding and routine operations.
Recovery Strategies After a Hijacking Attempt
Damage Control and Incident Response
If a hijack is detected, immediately change all credentials, revoke tokens, and restore from known clean backups. Notify customers if their data was affected and initiate forensic analysis to identify the source of the breach.
Legal and SEO Recovery Considerations
Submit reconsideration requests to search engines if your site was flagged or blocked. Work with legal teams if user data is exposed. Update all security measures to prevent repeat incidents.
Conclusion: Take Control Before Attackers Do
Knowing how to prevent website hijacking is not optional—it’s essential. Start by securing DNS, enforcing strong authentication, actively monitoring, and hardening all entry points. Regular testing, employee training, and responsive incident handling are your best defenses. Don’t wait for an attack to learn the hard way—secure your website now and build digital trust that lasts.













