If you believed phishing emails were the most straightforward cybersecurity threat, think again. A newer, more devious phishing tactic is gaining momentum in the cybercrime world—the BITB attack, an abbreviation for Browser-in-the-Browser. And no, it’s not just another jargon. This method is remarkably effective and doesn’t necessitate advanced hacking skills or expensive tools. BITB attacks exploit something we all use every day: our web browser. The simplicity of this attack should serve as a wake-up call for all of us to be more vigilant.
Let’s be honest—most of us click login windows on autopilot. See the familiar Google, Facebook, or Microsoft login popup? We type in our username and password without a second thought. BITB attacks count on that habit, mimicking these login prompts so convincingly that even security pros have been fooled.
In this article, we’ll dive deep into how BITB attacks work, why they’re so dangerous, and what you can do to stay safe. Whether you’re an IT admin, a business owner, or someone who wants to protect their personal data, this guide is for you.
What Is a BITB Attack?
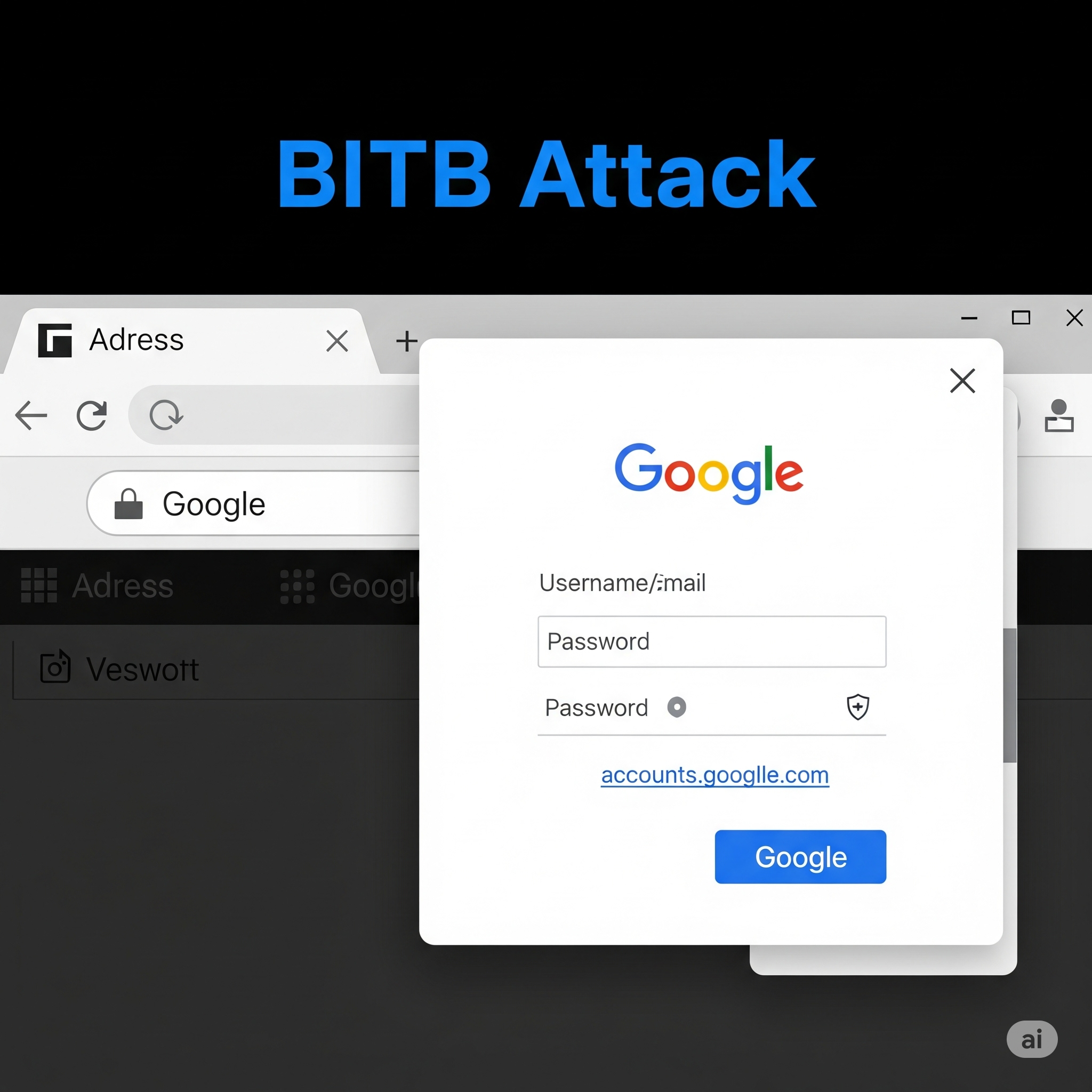
Let’s start by understanding what this threat really is. A Browser-in-the-Browser (BITB) attack is a type of phishing scam in which hackers create a fake browser window inside a legitimate web page. This imitation looks exactly like a real login popup—like the ones you see when you log into a site using your Google or Microsoft account.
The goal? Trick you into entering your credentials.
The attacker uses HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to design a pixel-perfect clone of a real authentication popup. To your eyes, it looks like a browser window. But it’s not. It’s a webpage designed to steal your login information.
What makes this so dangerous is how convincing it is. Since most of us trust familiar interfaces and are used to seeing popups during login flows, the attack easily slides under the radar.
A Quick History: Where Did BITB Attacks Come From?
While the concept sounds new, faking browser elements goes back years. However, the specific Browser-in-the-Browser technique gained attention in early 2022 when a security researcher published a detailed proof of concept.
That article went viral in cybersecurity circles. Suddenly, what was once a theoretical trick became a blueprint for real-world exploitation. Since then, multiple phishing campaigns have adopted this strategy, targeting individuals and corporations.
Unlike traditional phishing, which often relies on email links leading to lookalike sites, BITB attacks don’t need you to leave the original website. The fake login happens inside the same tab, making it even more deceptive.
How Does a BITB Attack Work?
The mechanics behind a BITB attack are surprisingly straightforward. Here’s how the scam usually unfolds:
- User clicks a login button – Say you’re trying to sign into a website using your Google credentials. You click “Login with Google.”
- Fake login popup appears—Instead of a real browser popup, a pre-rendered fake window appears. It includes the Google login interface with branding, form fields, and even a URL bar.
- You enter credentials. Thinking it’s legitimate, you type in your username and password.
- Credentials are captured – When you submit, your information is sent to the attacker’s server.
- Optional redirection – To keep the illusion alive, you may even be redirected to the actual login page afterward.
This trick doesn’t use an actual browser window. It’s just a smartly designed part of the webpage that looks like one. And that’s the genius—and danger—of it.

The Role of Social Engineering
The real power behind BITB attacks is sound old-fashioned social engineering. This attack preys on your expectations and habits. You’ve trained yourself to trust browser-based logins because they’re everywhere, and that’s exactly what the attacker is counting on.
They rely on psychology, not brute force. The scam’s success lies in the user not questioning what they see. Because everything looks “normal,” the victim doesn’t think twice.
In short, It’s not the tech that gets you—it’s the trick.
Why Are BITB Attacks So Effective?
Several factors make BITB attacks incredibly effective:
- Visual Accuracy – These fake windows look identical to the real ones.
- URL Bar Deception – Attackers can mimic browser UI elements, including the address bar.
- No Suspicious Redirects—Traditional phishing redirects you to a weird-looking URL, while BITB keeps you on the same page.
- MFA-Ready—Even multi-factor authentication (MFA) isn’t foolproof. Attackers can prompt for codes and immediately reuse them in real-time.
- Cross-Browser Compatibility – The attack works across Chrome, Firefox, and Edge.
Because users aren’t moved to a new tab or window, they don’t notice anything odd. Everything appears native.
Examples of BITB in the Wild
While many BITB attack examples remain under the radar, some have been spotted in campaigns targeting:
- Gamers – Login windows for Steam or Discord accounts
- Corporate Employees – Office365 and Google Workspace popups
- Developers – GitHub login pages
- Crypto Investors – Fake MetaMask login interfaces
In one case, a user clicked a fake Microsoft Teams link sent via chat. A BITB window asked for credentials. Within minutes, their corporate email was compromised, and malicious emails were sent from their account.
Real damage. Real fast.
The Real-World Impact of BITB Attacks
BITB attacks are not just about stolen logins. Once an attacker gains access, the fallout can include:
- Business Email Compromise (BEC) – Using internal emails to target others
- Data Theft – Downloading sensitive files or financial documents
- Lateral Movement – Gaining access to more systems within a network
- Account Takeover – Hijacking services like banking, social media, or cloud storage
- Ransomware Deployment – Locking down systems after initial access
For businesses, the cost isn’t just technical—it’s reputational and financial.
Detection Challenges: Why They’re Hard to Spot
Most phishing attempts leave digital breadcrumbs—suspicious links, mismatched domains, or odd formatting. But BITB? Not so much.
- No Link Redirection – Nothing to scan traditionally.
- Rendered Locally – The fake browser is on the same page, so security tools often miss it.
- No Downloads – No attachments or payloads that antivirus tools can flag.
- SSL Certificates Can’t Help – The real site might still use HTTPS, giving a false sense of safety.
All this makes BITB attacks incredibly tough to detect until it’s too late.
How to Prevent BITB Attacks
Fortunately, there are steps users and organizations can take to protect themselves:
- Educate Your Team – Awareness is the first line of defense. Teach employees how BITB attacks work and what to look for. By empowering your team with this knowledge, you can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to such attacks.
- Use Password Managers. These tools won’t autofill passwords on fake login windows because they detect that they’re not real browser popups.
- Enable MFA with Caution – While not foolproof, multi-factor authentication still adds a layer of protection.
- Inspect Login Windows – If you’re asked to log in, drag the popup window. It might be fake if it doesn’t move independently from the browser tab.
- Adopt Advanced Anti-Phishing Tools – Some enterprise security platforms now scan web elements for suspicious behaviors, including fake popups.
- Limit SSO Scope – If possible, restrict what users can authenticate with third-party services. Fewer points of entry mean fewer risks.
Future Trends: BITB and Beyond
BITB is just one example of how phishing tactics are evolving. Shortly, we might see:
- Mobile BITB – Adaptations targeting smartphones and tablets
- AI-Enhanced Phishing – More convincing bait messages using generative AI
- Deepfake UI – Browser elements mimicking entire applications
- Live Session Hijacking – Attacks that capture login data in real-time and initiate parallel sessions
As attackers get smarter, our defenses need to follow suit. Static security models won’t cut it.
Conclusion: Stay Sharp, Stay Safe
The Browser-in-the-Browser attack may seem simple, but its effectiveness makes it dangerous. It doesn’t break into your system—it waits for you to open the door. BITB tricks even the sharpest users into handing over their credentials on a silver platter by mimicking what’s familiar.
So what’s the best defense? Knowledge. Understand how the attack works. Share that knowledge. Stay skeptical of login windows—especially when they feel “too perfect.” If you’re managing a team or company, make BITB awareness part of your security culture.
In today’s digital world, the most dangerous threats aren’t brute force—they’re beautifully crafted illusions.













